The State of Homebuying in America
Overview
The American homebuying landscape has fundamentally shifted in the wake of aggressive Federal Reserve rate hikes, creating a complex environment where traditional purchasing patterns no longer apply. This comprehensive analysis of 1,000 recent homebuyers reveals not just what happened during their purchases, but exposes systemic vulnerabilities in how different generations approach homeownership in today's market.
The data reveals a troubling paradox: while homeownership remains a cornerstone of the American Dream, the path to achieving it has become increasingly fraught with financial risks that many buyers—particularly younger ones—may not fully comprehend. The survey uncovers a generation of buyers who are essentially gambling their financial futures on uncertain interest rate scenarios, while simultaneously struggling with confidence gaps that could have long-term implications for their economic stability.
Methodology and Survey Scope
This analysis is based on responses from 1,000 Americans who completed home purchases within the past 18 months, capturing experiences during one of the most volatile periods in recent real estate history. The survey period encompasses the transition from historically low rates to the current elevated environment, providing unique insights into buyer adaptation and decision-making under stress.
The timing of this survey is particularly significant, as it captures the experiences of buyers who navigated the market during historic socioeconomic uncertainty—those who bought when rates were rapidly rising and market dynamics (from unemployment and layoffs to Wall Street turbulence) were shifting monthly. These buyers represent a unique cohort whose experiences may preview broader market trends and potential systemic risks.
Critical Finding: The Refinancing Dependency Crisis
The Scale of the Problem
The survey's most alarming finding reveals that nearly two-thirds of Gen Z (64%) and Millennial buyers (65%) are banking their financial well-being on their ability to refinance to lower rates in the future. This represents more than double the dependency rate of Baby Boomers (32%), creating a generational financial fault line that could have far-reaching economic consequences.
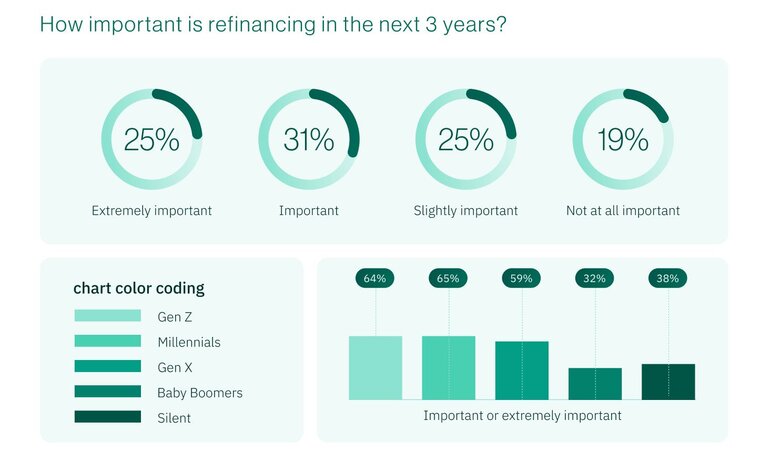
Key metrics:
- More than half – 56% – of all recent buyers consider refinancing important or extremely important to their financial wellbeing
- One in four or 25% of buyers consider refinancing ability "extremely important"
- The 32-percentage-point gap between young and older buyers represents the largest generational divide in the survey
Strategic Analysis: The Refinancing Gamble
This dependency on future refinancing opportunities represents a fundamental shift in homebuying strategy that warrants serious concern. Unlike previous generations who typically purchased homes with the expectation of maintaining their initial mortgage terms and with confidence in their ability to afford the current monthly payments for the foreseeable future, today's younger buyers are essentially making leveraged bets on Federal Reserve policy decisions.
This is risky business for several reasons, including:
- Policy uncertainty: Federal Reserve monetary policy is inherently unpredictable, with rate decisions driven by complex economic factors beyond housing market conditions. That said, mortgage rates are expected to only decline slightly in 2025 as the U.S. economy slows, with volatility caused by a number of variables such as tariffs, tax cuts and other aspects of President Donald Trump's economic agenda. As of July 2025, most experts (including analysts from Fannie Mae and the National Association of Realtors) predict the 30-year fixed mortgage rate to bounce between 6% and 7% for the next two years. However, that could change as investors continue to digest changing economic data.
- Qualification changes: Future refinancing eligibility depends on maintaining employment, income levels, and credit scores—factors that can change dramatically over the typical 5-7 year refinancing timeline.
- Market timing and costs: Even if rates do decline, timing the refinancing market optimally requires expertise that many homeowners lack. Most financial advisors say that refinancing really only makes financial sense if you can decrease your mortgage rate by at least 1%. When you refinance your mortgage, you’re on the hook to pay thousands of dollars in closing costs, so it's not worth the expense (and time involved) for only a minor reduction in your interest rate or small savings in your monthly payment—especially if there’s a chance rates will continue to go down or might decline further in the future.
Should rates remain elevated for an extended period of time, the possible implications for younger buyers—and the ripple effects on the economy—are troublesome. Specifically, we could see:
- People stuck in homes and unable to move due to rate lock-in effects
- Reduced discretionary spending as housing costs consume larger income portions
- Potential default risks if employment or income situations deteriorate
The Experience Gap: Difficulty and Expectations by Generation
First-Time Buyer Challenges: A Generational Divide
The survey reveals that younger buyers are not just facing higher costs—they're experiencing fundamentally different challenges that suggest systemic market changes rather than typical cyclical variations.
Difficulty perception by generation:
- Gen Z: 37% of first-time buyers found the process more difficult than expected
- Millennials: 32% found buying more difficult than expected
- Gen X: 19% found buying more difficult than expected
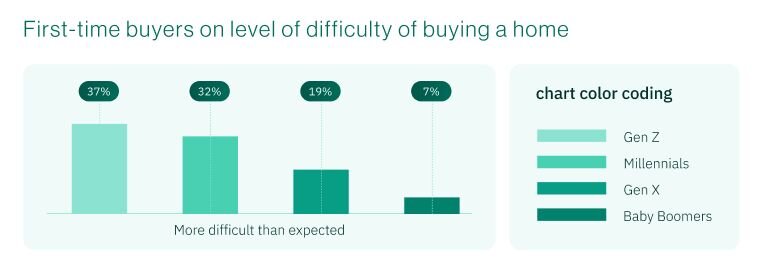
The 18-percentage-point gap between Gen Z and Gen X buyers indicates more than just market conditions. This suggests that younger buyers either had unrealistic expectations or that the market has fundamentally changed in ways that traditional advice and preparation don't address.
The Information Gap Problem
Younger buyers' higher difficulty rates may stem from several systemic issues:
- Digital information overload: While Gen Z and Millennials have unprecedented access to information, they may lack the contextual knowledge to distinguish between actionable advice and marketing content. These are buyers who have been raised with the habit of scrolling Zillow listings and home price data for fun and who receive personal finance and other types of advice via TikTok and Youtube.
- Peer network limitations: Unlike older generations who could rely on friends and family with home buying experience, younger buyers often have peer networks with limited real estate knowledge
- Market volatility: The rapid changes in rates, inventory, and competition created conditions where even recent advice became obsolete quickly
Regional Variations and Market Maturity
The finding that West Coast buyers (27%) were most likely to find the process more difficult than expected aligns with broader market dynamics in high-cost, high-competition markets. This suggests that market maturity and price levels may be creating increasingly complex buying processes that even experienced buyers struggle to navigate.
Financial Stress: Beyond Simple Affordability
The Psychological Toll of Modern Home Buying
The survey reveals that 90% of recent buyers experienced stress during the process, with 30% reporting "significant stress," numbers that seem to go beyond typical transaction anxiety and an actual, measurable toll on mental wellbeing. And while, the younger buyers experience higher levels of stress, it’s consistent across generations.
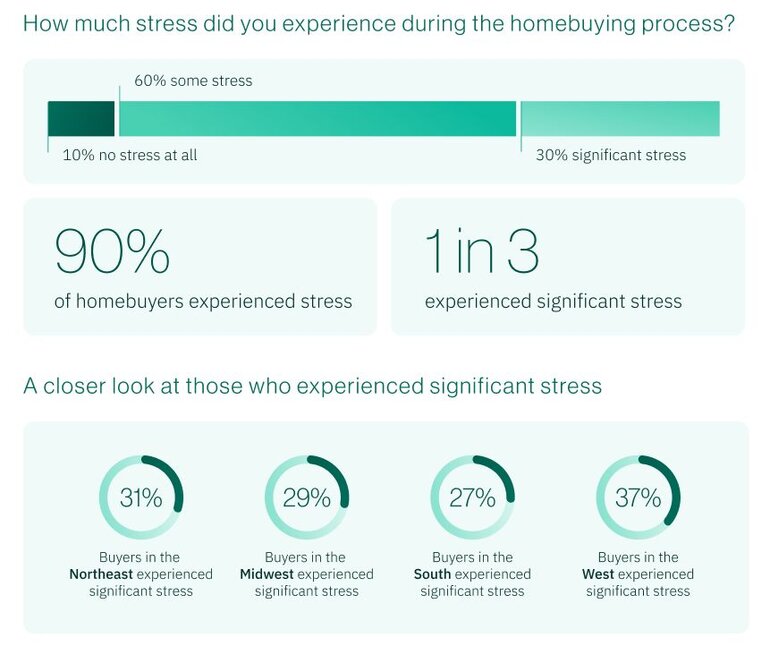
- Gen Z/Millennials: 33% experienced significant stress
- Gen X: 31% experienced significant stress
- Baby Boomers: 22% experienced significant stress
Regional stress patterns:
- West Coast: 39% significant stress
- South: 27% significant stress
- 12-percentage-point regional gap indicates market-specific pressures
Root Causes of Elevated Stress
The stress patterns reveal several concerning trends:
- Process complexity: The tie between "navigating paperwork" and "limited inventory" as top stressors (both 12%) suggests that both supply-side and regulatory factors are creating buyer friction
- Financial uncertainty: “Mortgage rates/affordability concerns” (11%) reflect the unprecedented rate environment buyers faced
- Timeline pressure: “Coordination challenges” (11%) indicate that multiple market participants are struggling to manage increased complexity
Generational Stress Responses
The different stress patterns by generation reveal distinct coping mechanisms and priority frameworks:
- Gen Z: Focus on rates/affordability (16%) shows acute awareness of cost pressures
- Millennials: Emphasis on competitive bidding situations reflects their experience in peak competition phases
- Gen X/Boomers: Coordination concerns suggest a preference for process control over cost optimization
Financial Hurdles: The Hidden Costs of Modern Home Buying
The Unexpected Expense Problem
The survey identifies "budgeting for unexpected expenses and repairs" as the top financial hurdle for recent buyers (17%), but this finding deserves deeper analysis. In a market where buyers are already stretching financially, the inability to anticipate and budget for standard homeownership costs suggests fundamental preparation gaps.
Top financial challenges:
- Unexpected expenses/repairs (17%): Process knowledge gaps
- Documentation gathering (16%): Regulatory compliance burden
- 20% down payment (15%): Capital accumulation challenges
The Documentation Burden: A Systemic Issue
The prominence of documentation gathering as a financial hurdle (16%) reflects broader regulatory and process changes that may be creating unnecessary barriers to homeownership. This is particularly pronounced among:
- Baby Boomers (20%): Likely struggling with digital processes and new requirements
- West Coast buyers (17%): Dealing with more complex state and local regulations
The documentation burden disproportionately affects buyers who may be financially qualified but lack the time, knowledge, or resources to navigate complex information requirements. This creates a two-tier system where process navigation skills become as important as financial capacity.
Regional Financial Challenges: Market-Specific Pressures
The regional variations in financial challenges reveal distinct market characteristics:
- Northeast: Unexpected closing costs (19%) suggest complex local fee structures
- South: Unexpected expenses/repairs (19%) may reflect different property conditions or inspection standards
- West: Documentation challenges (17%) likely reflect stricter regulatory environments
- Midwest: Balanced challenges suggest more stable, predictable markets
The Surprise Factor: Market Education Gaps
The Cost Surprise: Beyond Sticker Shock
The finding that 24% of buyers were surprised by additional costs (agent fees, inspections, closing costs) represents a significant market education failure. In an era of unprecedented information access, the persistence of cost surprises suggests either:
- Information quality issues: Available information may be incomplete or misleading
- Cognitive overload: Buyers may be overwhelmed by the volume of information and unable to process cost implications effectively
- Industry communication failures: Real estate professionals may not be effectively communicating the total cost of ownership
Timeline Surprises: Process Dysfunction
The 15% of buyers surprised by closing delays indicates systematic process inefficiencies that extend beyond individual transactions. This suggests:
- Capacity constraints: Industry infrastructure may be inadequate for current transaction volumes
- Coordination failures: Multiple market participants struggling to manage increased complexity
- Technology gaps: Despite digitalization efforts, process bottlenecks persist
The Privacy Surprise: Digital Age Concerns
The prominence of "private data requirements" as a surprise, particularly among younger buyers, reflects generational differences in privacy expectations. This finding suggests potential future friction as privacy-conscious generations become dominant buyer demographics.
Down Payment Strategies: Capital Access and Generational Wealth
The Savings Challenge
While 52% of buyers used personal savings for down payments, this figure masks significant generational disparities in capital access and accumulation strategies.
Down payment sources:
- Personal savings: 52% (but varies significantly by generation)
- Home equity: 28% (primarily repeat buyers)
- Investment Liquidation: 9% (higher among younger buyers)
- Family support: 7% (significantly higher among Gen Z at 14%)
Generational Wealth Transfer Patterns
The finding that 14% of Gen Z buyers received family gifts or loans (double the general population) reveals the increasing importance of intergenerational wealth transfer in homeownership access. This trend has significant implications:
- Inequality amplification: Buyers with family wealth have significant advantages in competitive markets
- Market distortion: Family support may be artificially inflating purchase prices in some segments
- Future dependency: Young buyers receiving family support may have different risk tolerances and financial planning approaches
- Lack of buyer independence: With a difficult job market, some younger buyers may lack the financial security of previous generations and rely on family to afford a home purchase
Investment Liquidation Trends
The 11% of Gen Z and Millennial buyers who liquidated stock holdings for down payments represents a potentially concerning trend. This strategy suggests:
- Opportunity cost acceptance: Buyers prioritizing homeownership over long-term investment returns
- Market timing risks: Stock liquidation during volatile periods may have resulted in suboptimal pricing
- Diversification concerns: Concentrating wealth in single real estate assets may increase overall financial risk
Purchase Motivations: The Urgency Factor
Homeownership at all costs
The dominance of "necessity" as a purchase motivation (32%) suggests that many buyers are being driven by life circumstances rather than investment opportunities. This has important implications for market stability:
Primary motivations:
- Life necessity: 32% (stable across generations)
- Price expectations: 21% (investment-driven)
- Emotional/cash position: 15% each (opportunity-driven)

The Price Expectation Factor
The 21% of buyers motivated by "prices not dropping, might increase" represents investment-driven purchasing that may be vulnerable to market corrections. This group likely overlaps with those dependent on refinancing opportunities, creating compound risk exposure.
Regional Motivation Patterns
The Northeast's unique focus on "rates will drop and we can refinance later" as a secondary motivation reveals regional variations in market sophistication and risk tolerance. This suggests that some markets may be more vulnerable to rate-dependent buyer behavior than others.
Confidence and Competence: The Knowledge Gap Crisis
Mortgage Understanding: A Fundamental Problem
The finding that 11% of buyers lack confidence in understanding mortgage terms represents a systemic market failure. In a transaction representing the largest financial commitment most people will make, this knowledge gap creates significant risks:
Confidence levels:
- All buyers: 11% lack confidence in mortgage terms
- Millennials: 15% lack confidence (highest among generations)
- Single women: 20% lack confidence vs. 10% for single men
The Gender Confidence Gap
The two-to-one gender disparity in mortgage confidence (20% vs. 10%) represents one of the survey's most concerning findings. This gap suggests:
- Systemic bias: Industry communication or education may not be effectively reaching women buyers
- Negotiation disadvantages: Lower confidence may translate to less favorable terms or reduced advocacy
- Long-term planning impacts: Confidence gaps may affect ongoing financial management and decision-making
Generation-Specific Confidence Patterns
The higher confidence gaps among younger buyers, particularly Millennials at 15%, suggest that despite greater access to information, actual comprehension and confidence are declining. This paradox may reflect:
- Information quality issues: More information doesn't necessarily mean better information
- Complexity increases: Modern mortgage products and processes may be inherently more complex
- Educational gaps: Traditional financial education may not address current market realities
Financial Security and Future Outlook: Warning Signs
Post-Purchase Financial Anxiety
The survey reveals troubling patterns in post-purchase financial outlook that suggest many buyers may have overextended themselves:
Security levels:
- Felt secure when buying: 86% (but only 19% felt "very secure")
- Feel optimistic about future: 82% overall
- Gen Z future pessimism: 27% (versus 16% average)
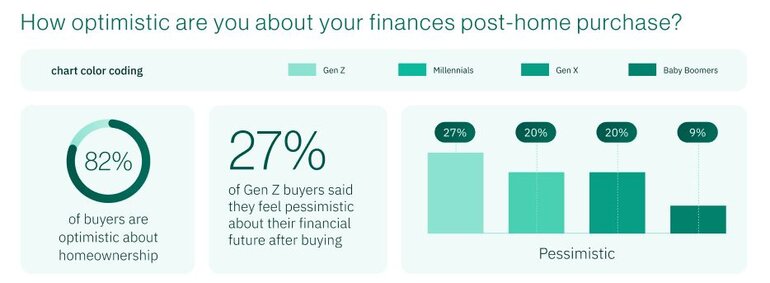
The Gen Z Pessimism Problem
The finding that 27% of Gen Z buyers feel pessimistic about their financial future after buying represents a potential crisis in confidence that could have broader economic implications. This level of post-purchase regret or concern suggests:
- Overextension: Buyers may have purchased beyond their comfortable financial capacity
- Expectation misalignment: The reality of homeownership costs may exceed expectations
- Market timing concerns: Buyers may recognize they purchased at suboptimal times
Security vs. Optimism Disconnect
The gap between feeling secure when buying (86%) and feeling optimistic about the future (82%) suggests that the homebuying process itself may be creating financial anxiety. The 4-percentage-point difference, while small, indicates that the transaction experience is affecting buyer confidence in their financial decision-making.
Market Implications and Systemic Risks
The Refinancing Time Bomb
The concentration of refinancing-dependent buyers, particularly among younger demographics, creates several systemic risks:
Immediate risks:
- Market liquidity: Rate lock-in effects may reduce transaction volumes
- Consumer spending: Higher housing costs may reduce discretionary spending
- Employment sensitivity: Job market changes could trigger cascading defaults
Long-term risks:
- Generational wealth: Younger buyers may struggle to build equity if unable to refinance
- Market segmentation: Different rate environments may create distinct buyer classes
- Political pressure: Widespread refinancing difficulties could drive policy interventions
Regional Vulnerability Patterns
The survey reveals that certain regions may be more vulnerable to market corrections:
- West Coast: Higher stress levels and difficulty rates suggest stretched buyer conditions
- Northeast: High refinancing dependency could create localized market instability
- South: More balanced conditions may provide market stability
Industry Adaptation Needs
The survey findings suggest several areas where industry adaptation is needed:
- Education enhancement: Better buyer education programs focused on realistic expectations
- Process simplification: Reducing documentation and coordination burdens
- Communication improvement: Gender-specific and generation-specific outreach strategies
- Risk assessment: Better tools for evaluating buyer financial resilience
Recommendations and Strategic Outlook
For Industry Professionals
Real estate agents:
- Implement comprehensive buyer education programs that address realistic cost and timeline expectations
- Develop generation-specific communication strategies that address distinct risk tolerances and information preferences
- Create post-purchase support systems to help buyers navigate ongoing homeownership challenges
Mortgage lenders:
- Enhance financial literacy programs with specific focus on mortgage terms and long-term planning
- Develop stress-testing tools that help buyers understand payment scenarios under different rate environments
- Address gender confidence gaps through targeted educational resources and communication approaches
Policy makers:
- Consider regulatory reforms that simplify documentation requirements without compromising consumer protection
- Evaluate the effectiveness of current buyer education requirements and programs
- Monitor refinancing dependency trends for potential systemic risk implications
For Buyers and Market Participants
Current buyers:
- Develop financial plans that don't depend on refinancing opportunities
- Invest in comprehensive buyer education beyond basic affordability calculations
- Build emergency reserves that account for homeownership surprises and unexpected costs
Future buyers:
- Learn from current buyer experiences to set realistic expectations
- Develop multiple financial scenarios that account for different rate environments
- Prioritize financial education and confidence-building before entering the market
Market Outlook and Predictions
Based on the survey findings, several trends are likely to emerge:
- Continued generational stratification: Different generations will likely exhibit distinct buying patterns and risk tolerances
- Regional market divergence: Markets with higher buyer stress may experience greater volatility
- Technology integration: Industry pressure to simplify processes may accelerate digital transformation
- Policy evolution: Widespread buyer difficulties may prompt regulatory or policy responses
Conclusion: Navigating an Uncertain Future
The Truework Recent Homebuyer Survey reveals a market in transition, where traditional assumptions about home buying no longer apply. The data exposes a generation of buyers who are taking unprecedented financial risks based on uncertain assumptions about future market conditions, while simultaneously struggling with confidence gaps that may compound their vulnerability.
The survey's findings suggest that we are witnessing not just a cyclical market adjustment, but a fundamental shift in how Americans approach homeownership. The combination of elevated financial stress, generational divides, and systemic process inefficiencies creates a complex environment that requires careful navigation by all market participants.
Key takeaways:
- Financial risk concentration: The heavy dependence on refinancing among younger buyers creates systemic vulnerabilities that could have broader economic implications
- Education and confidence gaps: Persistent knowledge gaps, particularly among women and younger buyers, suggest industry-wide communication failures
- Process dysfunction: High stress levels and surprise rates indicate that current market processes are inadequate for buyer needs
- Regional variation: Different markets are experiencing distinct pressures that may require tailored solutions
Looking forward:
The home buying landscape will likely continue evolving as market participants adapt to current conditions. Success will require:
- Realistic expectations: Buyers must plan for current market realities rather than optimal scenarios
- Enhanced education: Industry professionals must improve buyer preparation and ongoing support
- Process innovation: Systematic improvements in efficiency and communication are essential
- Risk management: All participants must develop better tools for assessing and managing financial risks
The American Dream of homeownership remains strong, but achieving it safely and sustainably in today's market requires new approaches, better education, and more sophisticated risk management than previous generations needed. The survey data provides a roadmap for these necessary adaptations, but implementation will require coordinated effort across the entire real estate ecosystem.
About this analysis
This comprehensive analysis is based on survey responses from 1,000 Americans who purchased homes within the past 18 months, representing experiences during one of the most volatile periods in recent real estate history. The findings provide unique insights into buyer behavior, market dynamics, and systemic risks that will shape the future of American homeownership.
Ready to unify your verification strategy?
Talk to our team about how Truework can help you reduce inefficiencies in your income verification process.